Powder coating has emerged as a popular finishing technique for a wide range of materials and products, thanks to its durability, efficiency, and environmental benefits. This advanced method not only provides an attractive finish but also protects surfaces from corrosion, wear, and UV damage. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the process of powder coating, its applications, types, advantages, and considerations.
Powder coating has emerged as a popular finishing technique for a wide range of materials and products, thanks to its durability, efficiency, and environmental benefits. This advanced method not only provides an attractive finish but also protects surfaces from corrosion, wear, and UV damage. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the process of powder coating, its applications, types, advantages, and considerations.
What Is Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a method of applying a decorative and protective finish to various substrates, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. Unlike traditional liquid paints, which contain solvents, powder coatings are composed of finely ground particles of pigment and resin. These particles are applied electrostatically and then cured under heat to form a solid, durable layer. This innovative process is particularly beneficial in both industrial and consumer applications, where high-quality finishes are required.
How Is Powder Coating Applied?
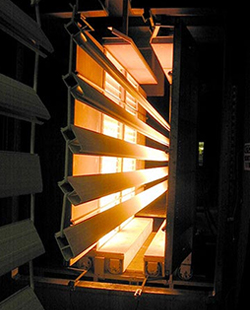
Electrostatic Spraying
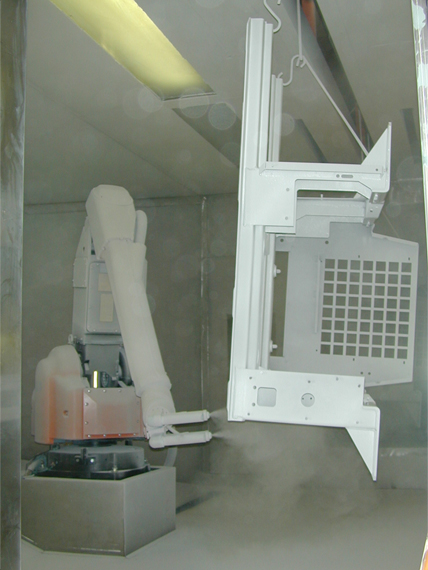
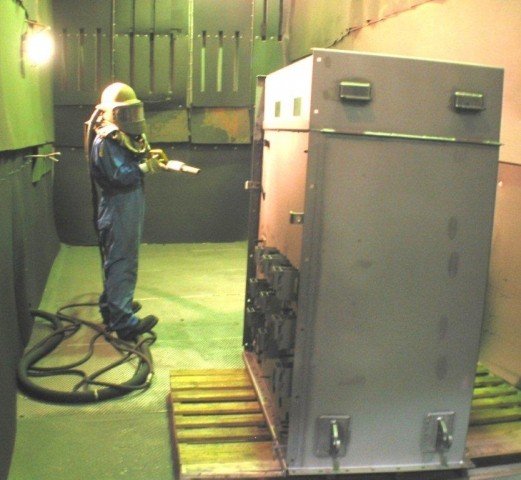
Electrostatic spraying is the most prevalent method for applying powder coatings. This technique involves using a powder gun that generates a high electrostatic charge (typically around 100 kV) on the powder particles. When these charged particles are sprayed onto a grounded surface, they adhere effectively due to the electrostatic attraction.
Once the powder is applied, the coated object is placed in a curing oven, where the heat causes the powder to melt and fuse, creating a smooth, uniform coating. This method is not only efficient but also reduces overspray and waste, making it an environmentally friendly choice. As a result, powder coating has become the fastest-growing finishing technology in North America, accounting for over 10% of all industrial finishing applications.
Fluid Bed Coating
Another method of powder coating is fluid bed coating, which utilizes a different approach. This technique involves placing powder in a chamber that is agitated to create a fluidized state. The powder expands, behaving like a liquid, allowing it to envelop preheated objects thoroughly.
The fluidized bed consists of two chambers separated by a porous membrane plate that diffuses air uniformly throughout the powder. This method is particularly effective for coating complex shapes, as the suspended powder can reach even the most inaccessible areas. Proper application results in complete encapsulation of the parts without sags, runs, or pinholes.
Types of Powder Coatings
Powder coatings can be categorized into two main types: thermoplastic and thermoset.
Thermoplastic Powder Coatings
Thermoplastic powders can be repeatedly softened by heat and hardened by cooling. This means that when a thermoplastic powder is heated, it undergoes a physical change rather than a chemical change. Some common types of thermoplastic coatings include:
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Known for its excellent chemical resistance and durability, PVC is often used in outdoor applications where protection from the elements is crucial.
- Nylons: These coatings are favored for their toughness and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for industrial applications.
- Polyolefins: This group includes polyethylene and polypropylene, which are used for their low friction properties and excellent chemical resistance.
Thermoset Powder Coatings
In contrast, thermoset powders undergo a chemical change when cured, transforming into an infusible and insoluble material. This change provides thermoset coatings with enhanced durability and chemical resistance. Common types of thermoset coatings include:
- Acrylics: Known for their clarity and weather resistance, acrylic powders are often used in automotive and architectural applications.
- Epoxies: These coatings are recognized for their strong adhesion and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for industrial environments.
- Polyesters: Polyester powders are popular for their color retention and flexibility, often used in both decorative and protective applications.
Advantages of Powder Coating
Powder coating offers several advantages over traditional liquid coatings, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers and consumers:
- Durability: Powder coatings are more resilient to chipping, scratching, and fading compared to conventional paints, providing long-lasting protection.
- Environmental Benefits: Since powder coatings do not contain solvents, they emit negligible volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them a more environmentally friendly option.
- Efficiency: The application process is more efficient, with less overspray and waste compared to liquid paints. This leads to reduced material costs and increased productivity.
- Variety of Finishes: Powder coatings are available in a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes, including matte, gloss, and metallic options, allowing for extensive customization.
- Uniform Coverage: The electrostatic application process ensures that powder coating provides uniform coverage, even in intricate shapes and hard-to-reach areas.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in equipment may be higher, the long-term savings due to reduced waste, fewer touch-ups, and increased durability can make powder coating a more cost-effective solution.
Applications of Powder Coating
Powder coating is versatile and can be used in a wide array of applications, including:
- Automotive Industry: Used for car parts, frames, and wheels, powder coating enhances both appearance and protection against corrosion.
- Architecture: Window frames, railings, and exterior cladding benefit from powder coatings’ durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Consumer Goods: Appliances, furniture, and electronics often utilize powder coating for its decorative finishes and protective qualities.
- Industrial Equipment: Machinery parts and tools are powder coated for enhanced wear resistance and longevity.
Considerations in Powder Coating
While powder coating has many benefits, there are also considerations to keep in mind:
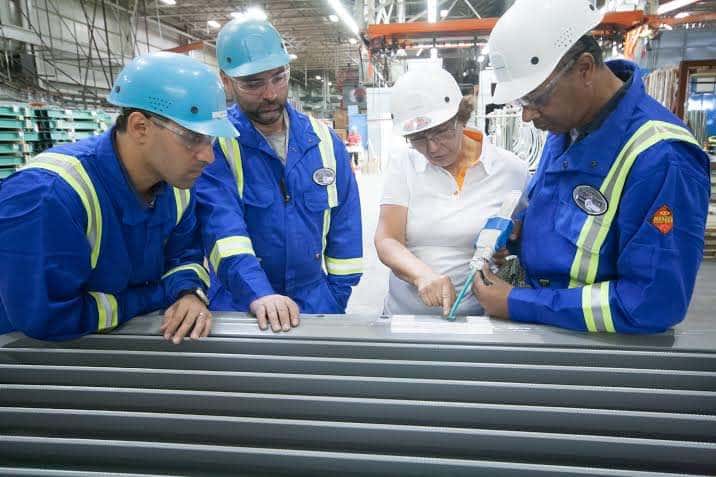
- Pre-treatment: Proper surface preparation is crucial for ensuring good adhesion. This often involves cleaning and degreasing the substrate before application.
- Curing Time and Temperature: The curing process requires precise control of temperature and time to achieve the desired finish. Variations can affect the quality and durability of the coating.
- Thickness: The thickness of the powder coat can be controlled, but excessively thick applications may lead to issues such as cracking or peeling.
- Equipment Costs: Setting up a powder coating system involves an initial investment in specialized equipment, which may be a consideration for smaller businesses.
- Color Matching: While there are many colors available, achieving an exact color match may be more challenging compared to liquid paints.
Conclusion
Powder coating is a modern, effective, and environmentally friendly finishing technique that offers numerous benefits across various industries. Its durability, efficiency, and aesthetic versatility make it an ideal choice for many applications, from automotive parts to consumer goods. Understanding the different application methods, types of coatings, and the advantages they offer can help manufacturers and consumers make informed decisions.
As the demand for sustainable and high-performance finishes continues to rise, powder coating is likely to remain a key player in the finishing industry, providing solutions that meet both functional and aesthetic needs. Whether you’re in manufacturing, construction, or simply looking to enhance the durability of your products, powder coating represents a smart investment in quality and performance.
Back